This article is more than 24 months old and is now archived. This article has not been updated to reflect any changes to the law.
Discretionary trust structures are widely used, particularly in family structures, for their tax saving benefits, in succession and estate planning, asset protection, access to CGT discounts and flexibility as to distribution of income and assets.
Come end of financial year the trustee must decide how to distribute the income of the trust which effectively determines who will pay tax on the trust's profits. Making distributions to a 'Bucket Company' can be used as a means to cap the amount of tax paid to 30%.
Melissa Ramov, Maddocks Lawyers1. What is a 'Bucket Company'?
A 'Bucket Company' structure establishes a Pty Ltd company (Bucket Company), which is an eligible beneficiary of an existing family discretionary trust (DT1). This enables the trustee of DT1 to distribute income to the Bucket Company from time to time.
The integration of a Bucket Company into an existing family trust structure can be illustrated by way of the following diagram and is explained in more detail in this article:
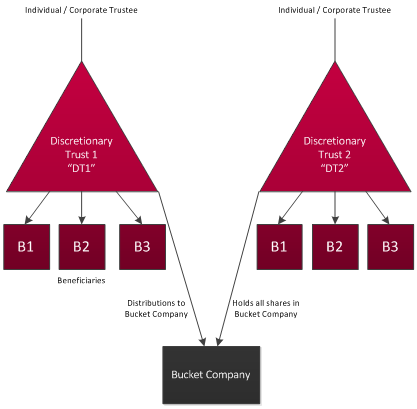
2. Why are they used?
Having a Bucket Company as an eligible beneficiary of a family trust allows the trustee to make distributions to the Bucket Company when other family beneficiaries have already used up their marginal tax rate of 32.5%. By distributing remaining income to the Bucket Company, this income will be taxed at the corporate rate of 30%.[1] The income will then remain in the Bucket Company until the Bucket Company decides to distribute the income to its shareholder(s) by way of a future dividend.
The only shareholder of the Bucket Company will be the trustee of a second discretionary trust (DT2) – a trust which is established for the purposes of receiving passive dividends from the Bucket Company and whose beneficiaries will be the same or similar persons who are the named beneficiaries of DT1 (shown in the above diagram as B1, B2, and B3).
Using this structure, the income of the Bucket Company can be ultimately distributed to the same beneficiaries of DT1 by way of fully franked dividends (i.e. the beneficiaries will not be required to pay tax on the proportion of the dividend which the Bucket Company has already paid tax). These distributions are made by the trustee of DT2 at a later time when the beneficiaries' marginal tax rates are near or below 30%.
3. Will my family trust structure allow a Bucket Company?
A Bucket Company will only be useful if, on registration, it becomes an eligible beneficiary of an existing family trust.One must read the trust deed of that trust to ensure that the Bucket Company will fall within the general class of beneficiaries. If your family trust deed is a standard Cleardocs deed then, provided the correct persons are directors or shareholders of the Bucket Company, then the Bucket Company will be within the class of eligible beneficiaries.
If the existing family trust:
- is not established through Cleardocs; or
- is established as a trust which prevents distributions to 'foreign persons'[2]
then you will need to ensure that your Bucket Company complies with these restrictions when it is established.
If your deed is a Cleardocs deed which only permits distributions to blood relatives of the named beneficiaries, then you cannot use the 'Bucket Company' product.
Cleardocs Bucket Company product
The Cleardocs Bucket Company product bundle includes the following documents:
- Company registration (establishing the Bucket Company);
- ABN registration for Bucket Company;
- Discretionary Trust set-up (establishing DT2);
- Discretionary Trust Distribution Minute – to record the distribution from DT1 to the Bucket Company; and
- 2 x Division 7A Loan Agreements – to record as a loan any distributions from DT1 to the Bucket Company which are declared but cannot be paid to the Bucket Company, and loans from the Bucket Company to the associates of its shareholder.
More information from Maddocks
For more information, contact Maddocks on (03) 9258 3555 and ask to speak to a member of the Commercial team.
More Cleardocs information on related topics
You can read earlier ClearLaw articles on a range of trust topics.
Order Cleardocs trust packages
- Discretionary (Family) Trust
- Discretionary Trust – excluded beneficiaries
- ABN Registration – trusts
- Unit Trust - fixed
- Unit Trust - non-fixed
- Hybrid Trust
- Change of Trustee Discretionary Trust
- Change of Trustee Unit Trust
- Discretionary Trust Distribution Minute
[1] Subject to legislative amendments to the corporate tax rate.
[2] This term is defined by reference to a range of definitions in Australian law including the duties act of each state and territory.
Lawyer in Profile

Lawyer
+61 3 9258 3201
sophie.edgar@maddocks.com.au
Qualifications: BA, LLB, Deakin University
Sophie is a member of Maddocks Commercial team. She is a corporate and commercial lawyer with a particular focus on:
- mergers & acquisitions,
- contract drafting,
- corporate restructures, and
- general corporate advisory.
She regularly assists clients across multiple sectors including consumer markets (beauty and retail), industrial (manufacturing and distribution) and financial services. Her private sector clients include multinationals, private equity funds and founders.
Read Our Latest Articles
customer support
legal advice
-

The legal information and commentary on this site is general only. Documents ordered through Cleardocs affect the user's legal rights and liabilities. To assess their suitability for the user, legal accounting and financial advice must be obtained.

